CS111 Lab 4:
Inheritance and Interfaces
Exercise 1: Fractal C-curve.
|
Use the MyMain() code below to test your application.
Classes needed for this app: Fractal.java, FractalCanvas.java, AppWindow.java, and MyMain.java.
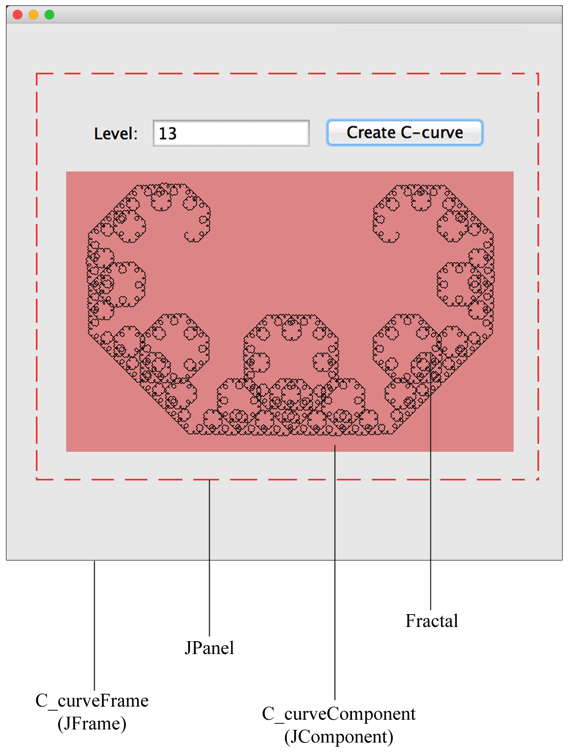
|
Part I: Graphical User Interface
|
This application will contain a graphical window as the top-level container.
It will measure 700 pixels in height and width.
The user interface components placed on this top-level container will include:
- JPanel container: This is lightweight container for components.
For example, a button
and a label component can be placed into a panel component.
- JLabel: Label for the input textfield component.
- JTextField: Input textbox for the user to specify a C-curve level.
Note: For numeric input, this string must parsed into a number value.
- JButton : To activate the drawing of a C-curve fractal.
Note: This button will be assigned an ActionListener.
- JComponent container: The drawing canvas for the C-curve fractal.
Note: JComponent includes an infrastructure for painting.
|
Fractal.java
import java.awt.Graphics;
public class Fractal {
public void drawCCurve(Graphics g, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int level) {
//PRIMITIVE STATE: DRAWS A STRAIGHT LINE FROM X1,Y1 TO X2,Y2
if (level == 1){
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
//RECURSIVE ELEMENT: TWO LINES WILL BE PRODUCED FOR EVERY SINGLE LINE
else {
int xn = (x1 + x2) / 2 + (y1 - y2) / 2;
int yn = (x2 - x1) / 2 + (y1 + y2) / 2;
drawCCurve(g, x1, y1, xn, yn, level - 1);
drawCCurve(g, xn, yn, x2, y2, level - 1);
}
}
}
FractalCanvas.java
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
//**************************************************************************
//FractalCanvas class is derived from the JComponent: This is the canvas.
//**************************************************************************
public class FractalCanvas extends JComponent {
// DATA MEMBERS: THE DRAWING COMPONENT
private Fractal fractal;
private int level;
private int x1, y1, x2, y2;
public FractalCanvas() {
level = 2;
fractal = new Fractal();
}
public void setXY(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
}
public void setLevel(int level){
this.level = level;
}
public void createCcurve() {
repaint();
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
fractal.drawCCurve(g, x1, y1, x2, y2, level);
}
}
AppWindow.java
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
//****************************************************************
// AppWindow class is derived from the JFrame
// Programmer: T. Cornez
//****************************************************************
public class AppWindow extends JFrame {
// TASK 1: DECLARE DATA MEMBERS
// NOTE: THESE WILL BE GUI ELEMENTS AND JPANEL THAT WILL BE PLACED
// IN THE WINDOW FRAME. JPANEL WILL BE USED TO HOLD THE GUI ELEMENTS.
private JPanel panel;
private JLabel levelLabel;
private JTextField levelTextField;
private JButton button;
private FractalCanvas fractalCanvas;
private final int WIDTH = 700;
private final int HEIGHT = 700;
// DEFAULT CONSTRUCTOR
public AppWindow() {
// TASK 1: SET THE WIDTH AND HEIGHT OF THE WINDOW FRAME TO 700
this.setSize(700, 700);
// TASK 2: INSTANTIATE THE JPANEL CONTAINER TO HOLD THE GUI ELEMENTS
panel = new JPanel();
// TASK 3: BUILD EACH GUI ELEMENT AND ADD THEM TO THE JPANEL
levelLabel = new JLabel("Level: ");
levelTextField = new JTextField(10); //FIELD WIDTH OF 10
levelTextField.setText("" + 2); //INITIALIZE THE TEXT FIELD TO 2
button = new JButton("Create C-curve");
// TASK 4: ADD EACH GUI ELEMENT TO THE PANEL
panel.add(levelLabel);
panel.add(levelTextField);
panel.add(button);
// TASK 5: INSTANTIATE THE DRAWING COMPONENT AND ADD IT TO THE JPANEL
fractalCanvas = new FractalCanvas();
fractalCanvas.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(WIDTH,HEIGHT));
fractalCanvas.setLevel(2); //The default level
panel.add(fractalCanvas);
// TASK 7: ADD THE COMPLETED PANEL TO THE FRAME WINDOW
this.add(panel);
// TASK 6: REGISTER AN ACTION LISTENER FOR THE BUTTON
ActionListener listener = new FractalActionListener();
button.addActionListener(listener);
}
class FractalActionListener implements ActionListener {
//Code this class.
}
}
Exercise 2: QuizApp additional Inheritance
|
Improve the Quiz App, from Lab 3, so that it consists of various types of questions, each modelled by a class: fill-in-the-blank (Question),
multiple choice (MultipleChoice), and true and false (TrueFalse).
Each question type inherits attributes from a superclass of Question.
- MultipleChoice inherits from Question
- TrueFalse inherits from MultipleChoice
- A MultipleChoice object stores the various choices for the answer. A method will be used for adding answer choices.
- When a MultipleChoice question is displayed to the user, the choices must appear so that the user can choose one of them.
- TrueFalse objects are MultipleChoice questions with only two options.
Use the MyMain() code below to test your application.
Classes needed for this app: MyMain.java, SalesSlip.java, and SalesItem.java.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MyMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TASK 1: INSTANTIATE THREE QUESTIONS, ONE FOR EACH TYPE.
// TYPE: GENERIC QUESTION
Question q1 = new Question("Who invented Java?", "James Gosling");
// TYPE: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
MultipleChoice q2 = new MultipleChoice("Year was Java born?", "");
q2.addChoice("1994", false);
q2.addChoice("1993", false);
q2.addChoice("1992", false);
q2.addChoice("1991", true);
// TYPE: TRUE OR FALSE QUESTION
Question q3 = new TrueFalse("Java is popular language.", "true");
// TASK 2: INSTANTIATE A QUIZ ENGINE AND POPULATE IT WITH QUESTIONS
QuizEngine quizEngine = new QuizEngine();
quizEngine.addQuestion(q1);
quizEngine.addQuestion(q2);
quizEngine.addQuestion(q3);
// TASK 3: SHUFFLE THE QUESTIONS AND START THE QUIZ
quizEngine.shuffleQuestions();
quizEngine.start();
quizEngine.getResults();
}
}
- Define a Java interface called Nameable
- Classes that implement this interface must provide the following:
- setName() method that requires a single String parameter and returns nothing
- getName() method that has no parameters and returns a String
