CS111 Lab 8
Exception Handling
File IO
Notes: Java includes two basic classes of errors: Exception and Error.
Exception
IOException
RuntimeException
ArithmeticException
IndexOutOfBoundsException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
NoSuchElementException
InputMismatchException
IllegalArgumentException
etc.
Error
VirtualMachineError
OutOfMemoryError
InternalError
etc.
Part I
Examine the code below.
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x, y;
int result;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
x = in.nextInt();
y = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("BLUE");
result = x / y;
System.out.println(result);
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Error RED");
}
catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("Error BLACK");
} finally {
System.out.println("GREEN");
}
}
}
Determine the output for the input below.
- 4 2
- 4.5 2
- 0 4
- 4 0
Part II
Exception Handling using throw
- Write a statement that throws an appropriate exception when the index for an array is out of bounds.
- Is the above statement a practical example of exception handling?
- What are good examples of exception handling?
Write a program to create a text file containing textual content. Try an ASCII bull's eye.
Use throws IOException to interrupt a failed I/O operation.
- Create an output file stream object, FileOutputStream, and link it to the text file.
- Write text to the file
- Close the file.
Write a program that reads from a text file and counts the number of paragraphs in the document.
Perform Exception Handling using throws IOException
- Go to the New York Times and copy the text for an article. Make sure the text contains at least three paragraphs.
Paste the text into a plain text (ascii text file) document (data.txt) and save it. Note the path.
- Recall that Scanners read from a given file or input stream.
Use throws IOException to interrupt a failed I/O operation.
The following tasks are used when reading from a file:
- Create a Scanner for performing input.
- Use the scanner to open an existing file for input.
- Close the file.
Write a program that accepts and displays an array of six integers.
Use a try/catch block to circumvent user data entry errors.
If the user enters a character or a floating-point number in response to a nextInt() method call,
the program should not crash.
Write a program that requires the user to input two integers, x and y.
Compute x divided by y.
The program must be able to catch two exceptions, one for arithmetic and one for InputMismatchException.
Write a program that reads from a text file and counts the number of words in the document.
Perform Exception Handling using try/catch
- Catch the exception when a file is not found: FileNotFoundException exception
- Catch the exception when a file contains invalid data: NoSuchElementException exception
Occasionally, action is needed whether or not an exception is thrown.
The finally construct is used to handle this situation.
Once a tryblock is entered, the statements in a finally clause are guaranteed to be executed,
whether or not an exception is thrown.
- Provide a program example that uses a finally clause.
- Test this example.
Examine the image below.
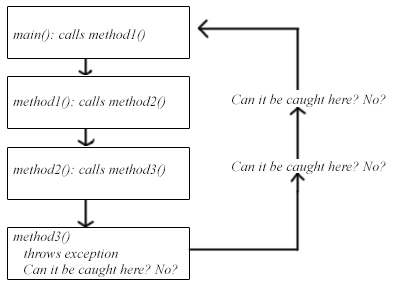
Provide a program that displays the printStack for an exception in this hierarchy.
Write an exception class for detecting an invalid exam score.

