public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//CREATE TOAST MESSAGES FOR THE EXPERIMENTS
private String createMsg;
private String startMsg;
private String resumeMsg;
private String pauseMsg;
private String stopMsg;
private String restartMsg;
private String msg;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initializeToastMsgs();
Toast.makeText(this, createMsg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Log.v(msg, createMsg);
}
private void initializeToastMsgs(){
createMsg = "Callback: onCreate()";
startMsg = "Callback: onStart()";
resumeMsg = "Callback: onResume()";
pauseMsg = "Callback: onPause()";
stopMsg = "Callback: onStop()";
restartMsg = "Callback: onRestart()";
msg = "activity callbacks ";
}
//************ override the callbacks to display Toast messages ****************
}
Exercise 2:
Create the app shown below. The goal of this app is to construct an app by researching online documentation. This app requires MediaPlayer for Android. Begin by creating a raw directory in the resources directory and loading it with an interesting sound. Test the app by playing the sound, pausing it, and then continuing to play it.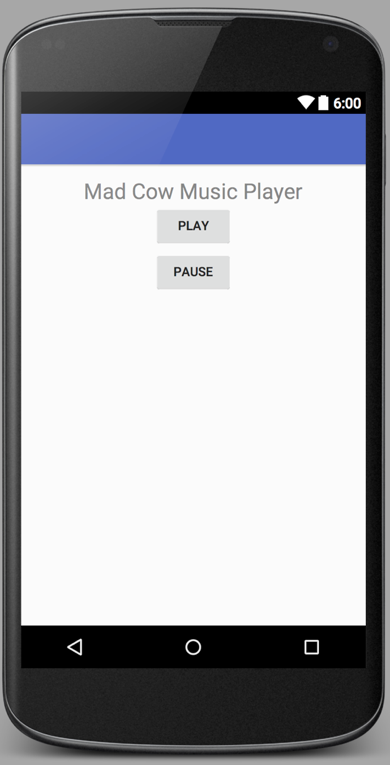
cow_mad_x.wav
Exercise 3:
Create the simple calculator shown below.Explore the use of a TableLayout.

Exercise 4:
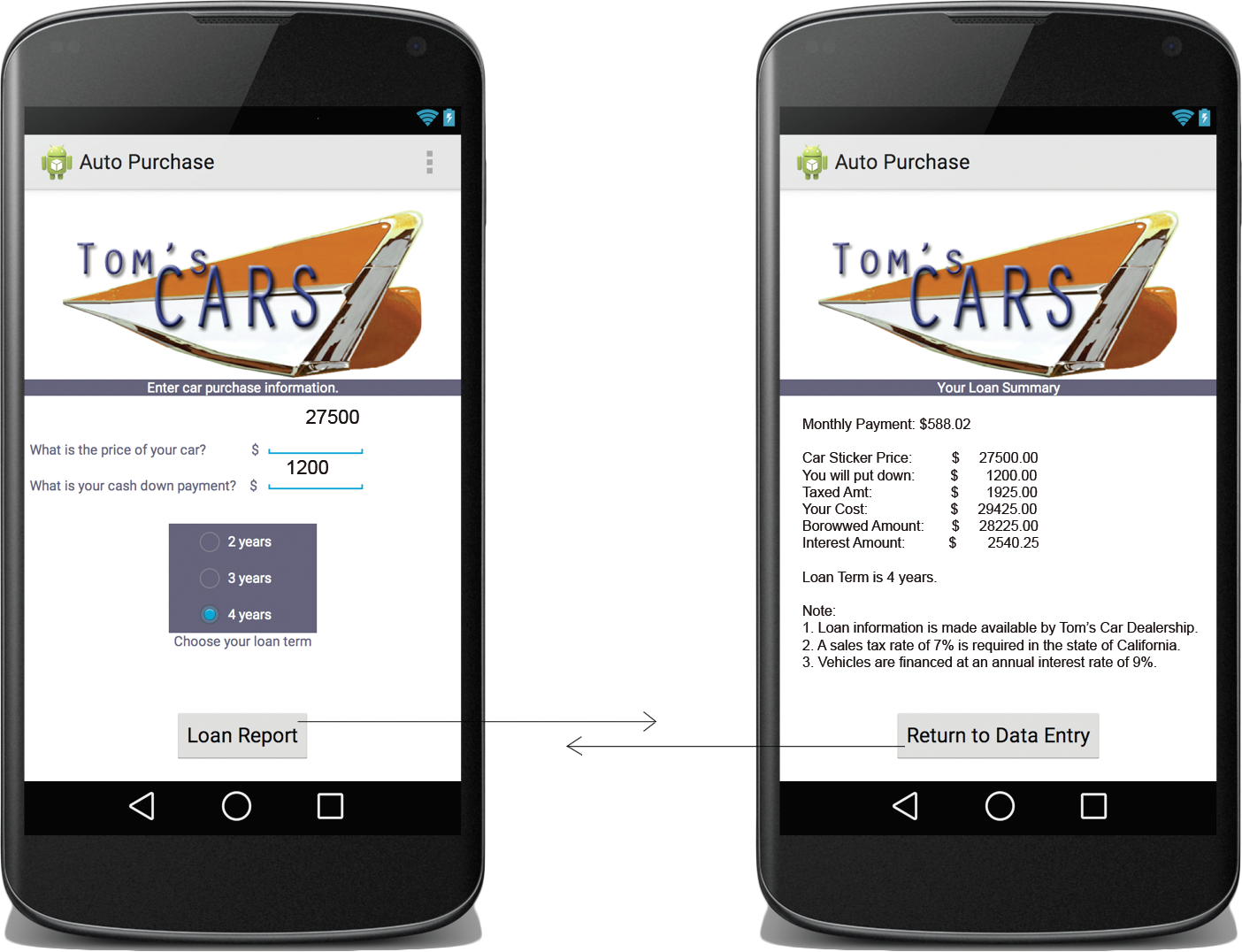
The goal of this app is to understand how data can be passed between activities within the same application.This Automotive Calculator App utilizes two user interface screens as follows:
- Input Activity: Allows the user to input car price, down payment and loan period.
- Loan Summary Activity:This activity is called to display the loan summary. It is passed the computed loan information and displays information in a scollable format.
Guidelines
- Design the app to allow the user to enter the price of a car (real), the down payment (real) and the number of years for the loan (integer).
- Calculate and output the monthly payment (real) of that car.
- Assume the sales tax rate is 7% and an interest rate is 9%.
- Use constant declarations for these rates.
-
Use the following formulae to perform the calculations:
-
tax amount = price of car * sales tax rate
total cost of car = price of car + tax amount
borrowed amount = total cost of car - down payment
interest amount = borrowed amount * interest rate
loan amount = borrowed amount + interest amount
monthly payment = loan amount / number of months of loan
- When displaying results, include detailed explanations so that the user understands what he/she
sees - Include the tax amount, borrowed amount, interest amount, and loan amount in your output in
addition to
the calculated monthly payments, the down payment and loan time.
Display dollar amounts as currency using $ and two decimal places.